Introducing CROC Level 4: Extending Cyber Risk Operations to the Digital Supply Chain
When I introduced the first three CROC Levels, the goal was to help organizations operationalize cyber risk management — from foundational visibility to strategic alignment. But as cyber risk becomes increasingly interconnected, it’s clear that managing your own risk is no longer enough.
Today, every organization operates within a complex web of suppliers, partners, and digital service providers. The next frontier in Cyber RiskOps is not just understanding your risk, but continuously quantifying the risk that comes from others.
CROC Level 4: Third-Party and Supply Chain Cyber Risk Operations
CROC Level 4 represents the evolution of cyber risk management beyond the organizational perimeter. At this stage, the Cyber Risk Operations Center doesn’t stop at internal telemetry—it extends its visibility and governance into the broader ecosystem of third-party vendors, managed services, and critical digital dependencies.
Capabilities at this level include:
Continuous monitoring of third-party attack surfaces using telemetry, threat intelligence, and exposure analytics.
Dynamic cyber risk scoring for each supplier, generating a real-time Cyber Risk Index (CRI) that reflects changes in their exposure, compliance posture, and threat activity.
Automated risk alerts and correlation when external partners experience incidents that could cascade into the organization’s environment.
Integration with procurement, legal, and compliance workflows to inform onboarding, contract renewals, and incident response with data-driven insights.
Cross-CROC collaboration between organizations for reciprocal risk visibility—turning isolated silos into a network of connected Cyber Risk Operations Centers.
At Level 4, the CROC becomes a living, adaptive system—one that doesn’t just measure internal resilience but continuously maps the cyber risk health of the entire digital supply chain.
The Cultural, Governance, and Contractual Shift
Achieving this level of maturity is not only a technological challenge—it’s a cultural transformation.
Organizations must evolve from isolated, compliance-driven interactions with suppliers to shared accountability for collective resilience.
That transformation requires three key shifts:
Cultural Change — Moving from secrecy to transparency.
Governance Change — Expanding the cyber risk governance model to include third-party oversight.
Contractual Change — Embedding cyber risk accountability into contracts.
Without these cultural, governance, and contractual foundations, Level 4 cannot truly exist. Technology can measure and automate—but only trust, shared governance, and enforceable agreements can sustain this ecosystem of continuous cyber risk operations.
The Cyber Risk Rating Era: From Annual Assessments to Real-Time Scoring
To understand where CROC Level 4 is taking us, imagine the world of credit ratings—but at the speed of cyber.
Credit rating agencies assess the financial health of companies, governments, and individuals based on historical performance, debt, and repayment behavior. These ratings guide investors, influence interest rates, and shape economic trust.
Now, replace “creditworthiness” with “cyber resilience.”
In the same way credit ratings measure the probability of financial default, the Cyber Risk Index measures the probability of digital disruption.
But unlike traditional ratings that are updated quarterly or annually, cyber risk changes by the minute—with every exposed API, misconfigured cloud bucket, or exploited dependency.
In this new model:
A supplier’s Cyber Risk Score could fluctuate daily based on emerging vulnerabilities, ransomware campaigns, or compliance deviations.
Boards could visualize the cyber health of their supply chain with the same precision that CFOs monitor financial liquidity.
Insurers, auditors, and regulators could rely on objective, continuous metrics instead of static self-assessments.
CROC Level 4 makes this vision operational. It transforms risk measurement into a real-time feedback system, where trust is earned, monitored, and maintained through transparency and performance—not assumptions or paperwork.
We are entering the Cyber Risk Rating Era — where resilience, like credit, becomes a measurable and tradable form of confidence.
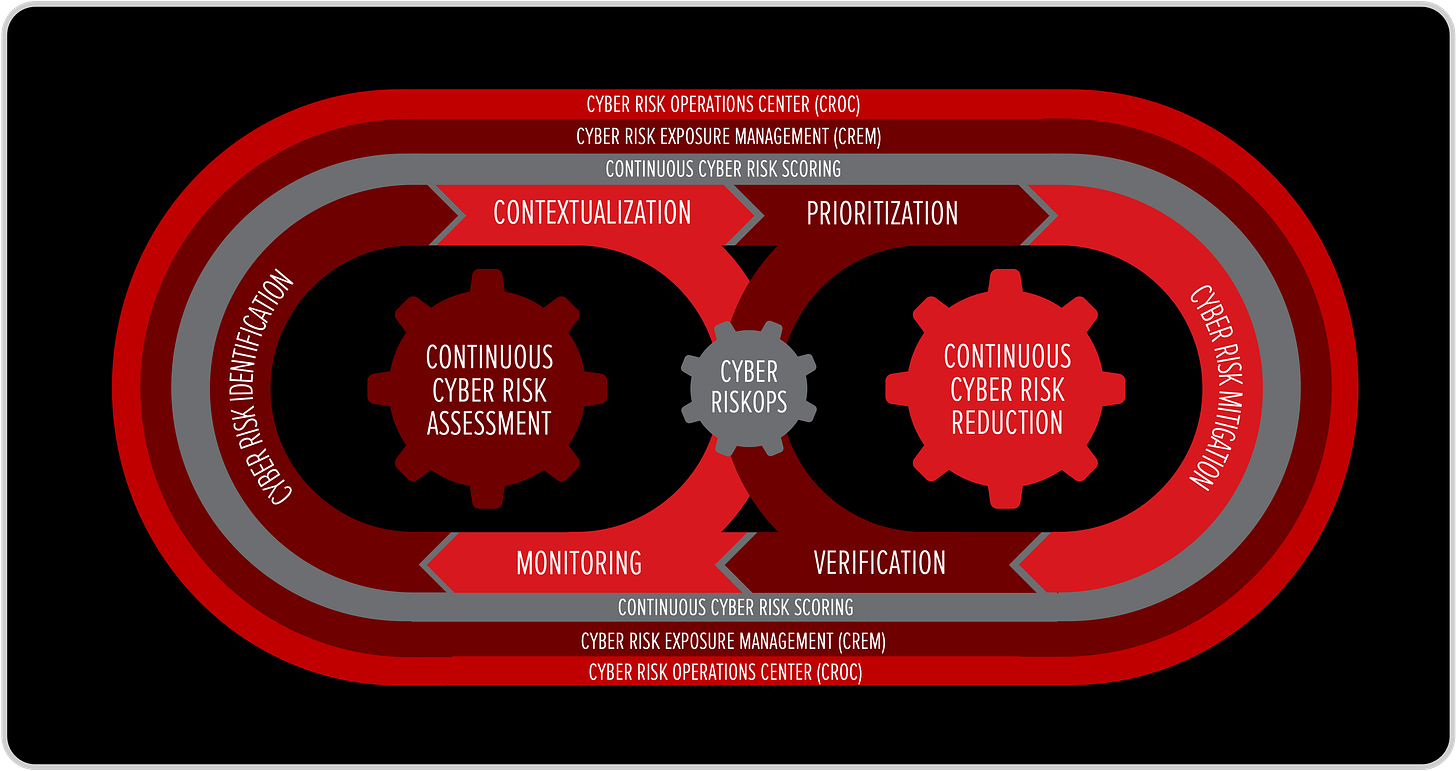
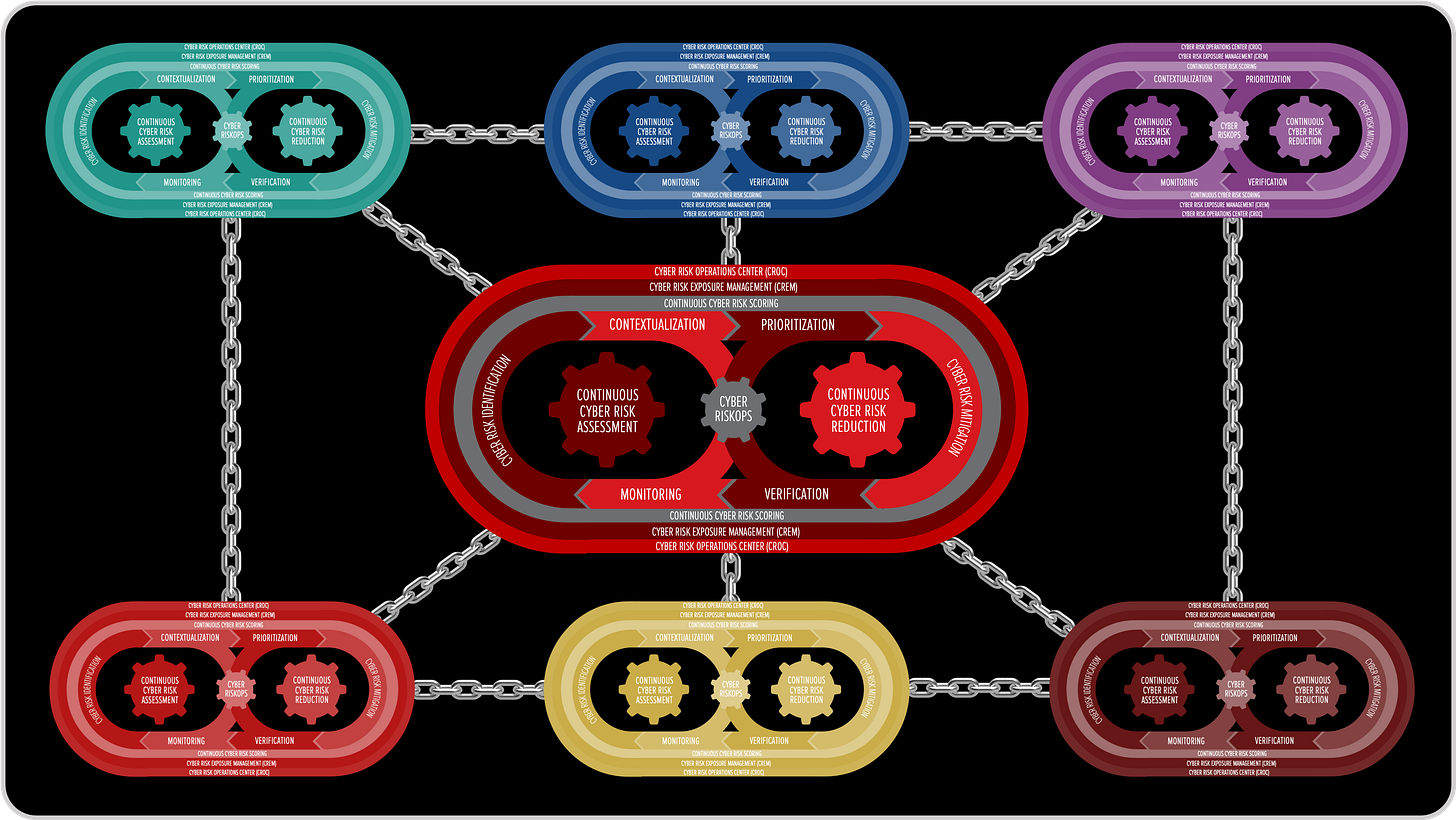
Cyber RiskOps Across the Digital Supply Chain
At CROC Level 4, the principles of Cyber RiskOps extend beyond the organization’s perimeter to encompass the entire digital supply chain. Every supplier, partner, and technology provider becomes part of a distributed Cyber Risk Operations Network, where each node runs its own Cyber RiskOps loop — or is continuously monitored by the CROC of the company that depends on it.
In this model:
Each participant ideally operates its own Cyber RiskOps cycle — contextualizing, prioritizing, monitoring, and verifying its own exposures and controls.
When a third party doesn’t yet operate a CROC, the CROC of the contracting organization assumes the monitoring role, continuously assessing that supplier’s cyber posture through external telemetry, attack surface data, and exposure scoring.
The company’s CROC correlates all these internal and external signals to compute a dynamic Cyber Risk Index (CRI) across the full supply chain, alerting leadership when a partner’s risk posture begins to drift or when systemic dependencies emerge.
This hybrid approach allows organizations to extend cyber risk governance without overstepping ownership boundaries.
Each supplier remains accountable for its own operations, but the primary organization maintains visibility and continuity — ensuring that the absence of a partner CROC never becomes a blind spot.
Over time, this model creates a federated ecosystem of Cyber RiskOps, where CROCs across industries collaborate, share risk intelligence, and synchronize defense.
Cyber risk becomes a shared operational fabric, not a fragmented responsibility — transforming supplier oversight from a compliance checklist into a continuous ecosystem resilience mechanism.
From Internal Awareness to Ecosystem Resilience
Reaching this level demands more than data integration; it requires redefining what “resilience” means in a connected world. Cyber resilience becomes an ecosystem metric—shared, monitored, and dynamically updated. Boards and executives gain a real-time view of supplier cyber risk exposure, transforming third-party management from a static audit checklist into an operational discipline.
This evolution turns the CROC into a Cyber Risk Nerve System—detecting, correlating, and quantifying not just internal vulnerabilities but external dependencies that shape the organization’s true resilience.
CROC Level 4 marks the beginning of an interconnected future where Cyber RiskOps becomes collaborative, proactive, and ecosystem-driven—where organizations don’t just protect themselves, but strengthen the resilience of the networks they depend on.
++++++
Castro, J. (2024). From Reactive to Proactive: The Critical Need for a Cyber Risk Operations Center (CROC). ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388194441 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.27408.93445/1
Castro, J. (2025). Cyber RiskOps: Bridging Strategy and Operations in Cybersecurity. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388194428 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.36216.97282/1
Castro, J. (2024). Integrating Cyber Risk Management to your Cybersecurity Strategy: Operationalizing with SOC & CROC. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388493453 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.30164.72328/1
Castro, J. (2024). Integrating NIST CSF 2.0 with the SOC-CROC Framework: A Comprehensive Approach to Cyber Risk Management. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388493049 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.13387.50720/1
Castro, J. (2025). Cyber Risk Operations Center (CROC) Process and Operational Guide. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/389350613 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.19164.09600
Castro, J. (2025). What Is Strategy in Cybersecurity? Rethinking the Way We Lead, Protect and Adapt. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/393674625 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.16703.42409
Castro, J. (2025). What Cybersecurity Can Learn from Glucose Management in Diabetes. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388528830 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.14003.54568/1
Castro, J. (2025). Introducing the CROC Levels: Operationalizing Cyber Risk Management. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/393333383 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.31393.31841
Castro, J. (2025). How a Cyber Risk Index (CRI) Can Be Used as a KPI in Your Cybersecurity Strategy. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/389001302 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.32915.18728
Castro, J. (2025). Cyber Risk Operational Model (CROM): From Static Risk Mapping to Proactive Cyber Risk Operations. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/390490235 DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.15956.92801